Wired vs Wireless Networking | Pros, Cons & Use Cases
When setting up a computer or connecting to the internet, you usually choose between wired and wireless networking.
But which is better—and why?
Let’s compare Ethernet (wired) and Wi-Fi (wireless) to help you decide.
What Is a Wired Network?
A wired network uses Ethernet cables to physically connect devices to the router, modem, or switch.
Example: Your PC plugged into the router using a LAN cable.
Related: What Is a Computer Network?
Related: Types of Networks: LAN, WAN, MAN
What Is a Wireless Network?
A wireless network uses Wi-Fi signals to connect devices without cables.
Example: Your phone or laptop connects to the internet via a home Wi-Fi router.
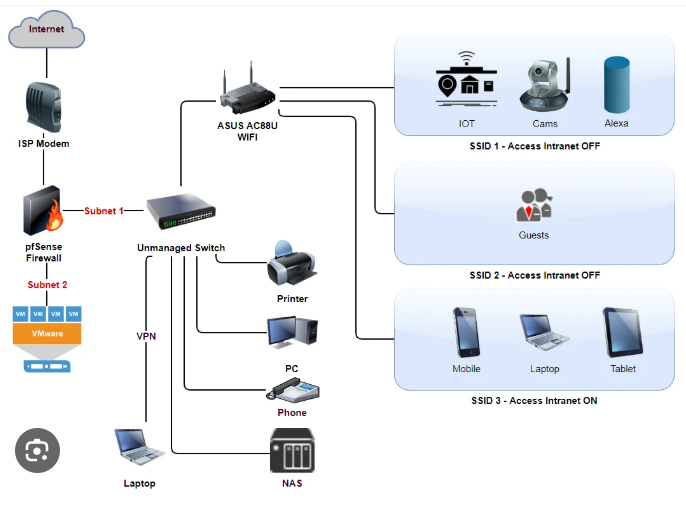
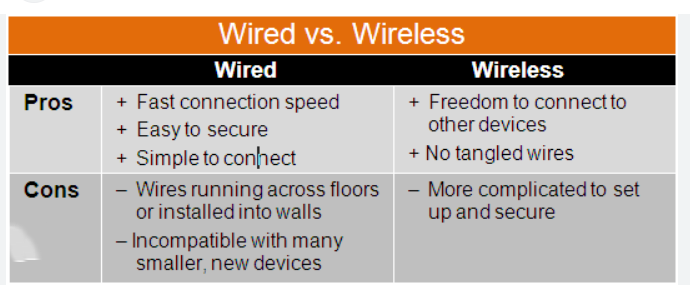
Wired vs Wireless: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Wired (Ethernet) | Wireless (Wi-Fi) |
| Speed | Faster and more consistent | Slower, may vary with distance |
| Stability | Highly stable, no interference | Can drop due to walls, signals, etc. |
| Security | More secure (physical access needed) | Can be hacked if not protected |
| Mobility | Limited – not portable | Full mobility |
| Setup | Requires cables and ports | Easy, no cables needed |
| Latency | Lower latency (great for gaming) | Higher latency (depends on signal) |
Speed & Interference: Which One Performs Better?
- Wired offers higher speeds and lower latency, making it ideal for:
- Online gaming
- Streaming in 4K
- Video conferencing
- Large file transfers
- Wireless is convenient but:
- Suffers from signal interference (walls, microwaves, other Wi-Fi networks)
- Speeds vary with distance from router
- Great for casual browsing, smart devices, and mobility
Common Use Cases
✔ Wired Networking
Best for:
- Offices or desktops needing speed
- Gamers and streamers
- Servers and media centers
- Environments requiring stable connections
✔ Wireless Networking
Best for:
- Homes and mobile devices
- Students and laptops
- Phones, tablets, and IoT devices
- Spaces where running cables is difficult
Quick Security Tip
Wired networks are harder to hack since they require physical access.
For wireless, always secure your Wi-Fi with a strong password and encryption (like WPA3).
Summary Table
| Use Case | Recommended Option |
| Gaming & Streaming | Wired |
| Casual Web Browsing | Wireless |
| Work-from-Home (Stable Zoom) | Wired |
| Moving Around Home | Wireless |
| File Transfers (Fast) | Wired |
💬 Have questions about setting up a home network or want a visual comparison chart?
Drop a comment or request it—I’ll add it for you!
Would you like me to create an infographic comparing Ethernet vs Wi-Fi visually?