Computers have come a long way since their early beginnings. Understanding the different generations of computers helps us see how technology evolved—from massive, vacuum-tube machines to today’s intelligent, AI-powered systems.
🕰️ To understand how computers evolved over time, it’s helpful to know where it all began.
👉 Read: The Early History of Computers: From Counting Tools to Machines
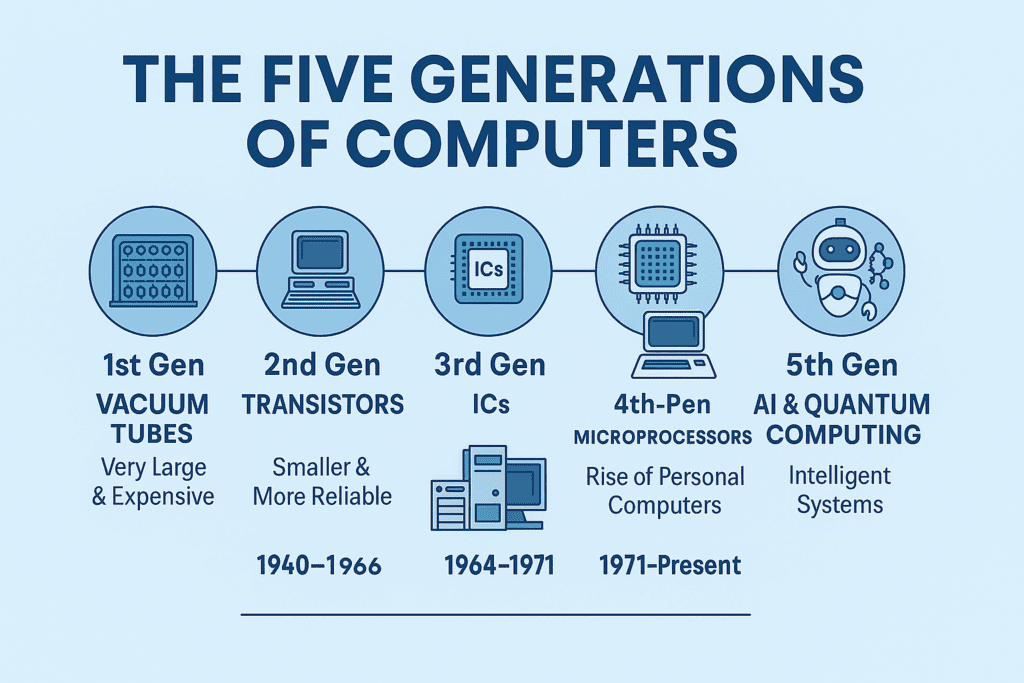
🧮 1st Generation (1940–1956): Vacuum Tubes
The first generation of computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. These machines were enormous, consumed a lot of power, and generated heat.
Key Features:
- Used machine-level programming
- Bulky and expensive
- Input/output via punch cards and paper tape
Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC
These early machines were the first real step in replacing manual calculations with automated processes.
👉 Learn more in the history blog
🔁 2nd Generation (1956–1963): Transistors
With the invention of the transistor, computers became smaller, faster, and more reliable.
Key Features:
- Used assembly language
- Stored programs in memory
- Improved energy efficiency
Examples: IBM 1401, CDC 1604
Programming became more accessible with the rise of high-level languages.
👉 Explore: What is Software? A Simple Guide for Beginners
🖥️ 3rd Generation (1964–1971): Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits (ICs) replaced transistors, leading to smaller and more efficient computers.
Key Features:
- Supported multitasking
- Used keyboards and monitors
- Expanded commercial use
Examples: IBM System/360, PDP-8
Software development took a leap forward during this generation.
👉 Discover the basics of application software
💾 4th Generation (1971–Present): Microprocessors
The microprocessor revolutionized computers by integrating thousands of ICs into a single chip. This led to the personal computer (PC) revolution.
Key Features:
- Graphical user interfaces (GUI)
- Widespread use of operating systems
- Rise of networking and the internet
Examples: Apple II, IBM PC, modern desktops/laptops
🤖 5th Generation (Present & Beyond): Artificial Intelligence
Fifth-generation computers aim to bring human-like thinking to machines through AI and machine learning.
Key Features:
- Natural language processing
- Neural networks and robotics
- Cloud and quantum computing
Examples: Smart assistants (like Siri, Alexa), AI-powered analytics tools
🧠 Conclusion
Understanding the five generations of computers gives insight into how far technology has come and where it might go next.
Want to dive deeper into how these systems actually work?
👉 Read: How Computers Work – A Beginner’s Guide