Network Topologies Explained | Star, Bus, Ring & Mesh
When building or understanding a network, one key concept to know is network topology—the layout of how devices (nodes) are connected. Whether you’re setting up a small office network or studying for your IT exam, understanding topologies is essential.
Let’s break it down in a simple and visual way.
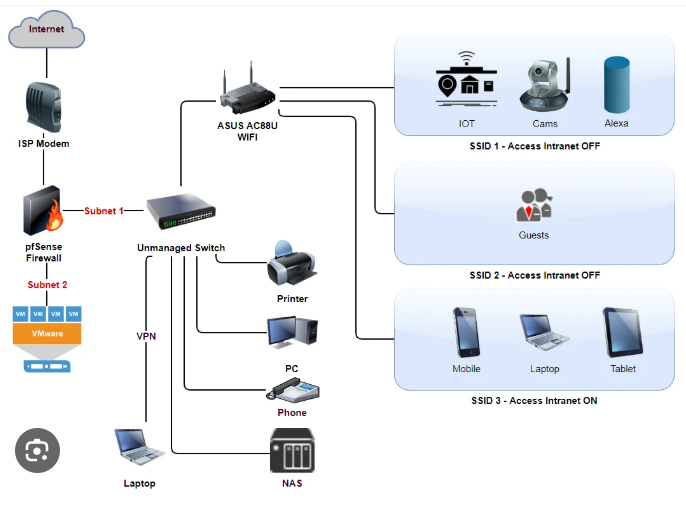
What is a Network Topology?
A network topology refers to the structure or arrangement of devices in a computer network. It determines how data flows between devices and how they are physically or logically connected.
There are several types of network topologies, each with its own advantages and limitations.
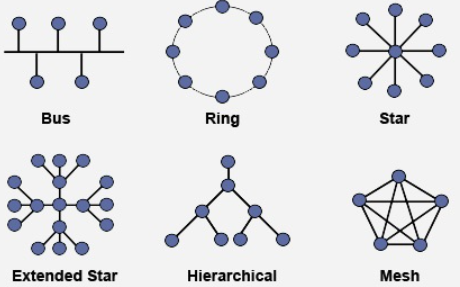
1. Star Topology
In a Star topology, all devices connect to a central hub or switch.
Real-life analogy:
Think of it like a wheel with spokes—the central hub is the wheel, and each spoke is a cable connecting to a device.
Pros:
-
Easy to add/remove devices
-
If one cable fails, the rest of the network stays up
Cons:
-
If the central hub fails, the whole network goes down
Related post: Networking Devices Explained
2. Bus Topology
In a Bus topology, all devices share a single communication line (a backbone cable).
Pros:
-
Easy and inexpensive to set up
-
Works well for small networks
Cons:
-
Data collisions are common
-
If the backbone fails, the entire network crashes
Learn more: What is a Computer Network?
3. Ring Topology
In a Ring topology, each device connects to two others, forming a circular path for signals.
Pros:
-
Data flows in one direction, reducing collisions
-
Good for predictable traffic
Cons:
-
A failure in any one cable/device breaks the loop
Helpful read: Types of Computer Networks
4. Mesh Topology
In a Mesh topology, every device connects to every other device.
Pros:
-
Extremely reliable and fault-tolerant
-
High redundancy and data security
Cons:
-
Complex and expensive to implement
-
Not practical for small networks
Related concept: Wired vs Wireless Networks
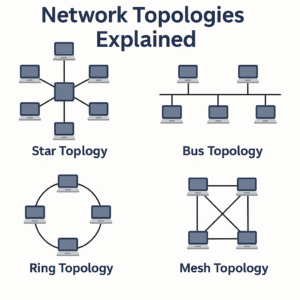
Visual Infographic
This image shows how each topology looks in a network setup.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right topology depends on your network’s size, budget, and performance needs. For small homes, a star or bus layout is common. For larger, mission-critical systems, mesh might be the way to go.
Got Questions?
Which topology is used in your home or office?
Leave a comment below — I’d love to hear your setup or help you figure it out!