What is the Internet? | How It Works in Simple Terms
Whether you’re browsing a website, streaming a video, or sending an email — you’re using the internet. But what is it really? And how does it work?
In this post, we’ll explain:
- What the internet is
- How it differs from an intranet
- Basic architecture (ISPs, servers, clients)
- Simple examples you can relate to
What Is the Internet?
The internet is a massive global network of computers connected through cables, satellites, and servers that allow people to share information and communicate instantly.
Think of it like a worldwide web of highways where data travels from one device to another — fast.
Every time you open a webpage, your device is connecting to another computer (called a server) somewhere in the world.
If you’re new to networks, check out
What Is a Computer Network?
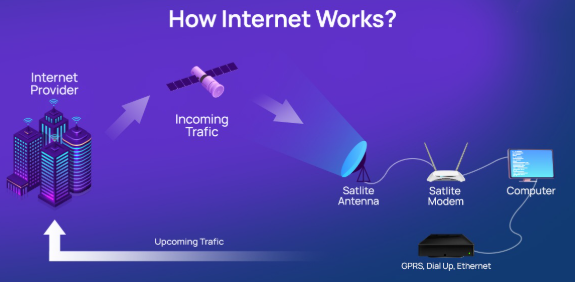
How Does the Internet Work?
Here’s a simplified flow of what happens when you visit a website:
- You type a website like www.exploretoday.blog
- Your browser asks your ISP (Internet Service Provider) where to find it
- The ISP contacts a DNS server to get the website’s IP address
- Your device connects to the web server that hosts the site
- The website’s data is sent back to you and displayed on your screen
All of this happens in milliseconds!
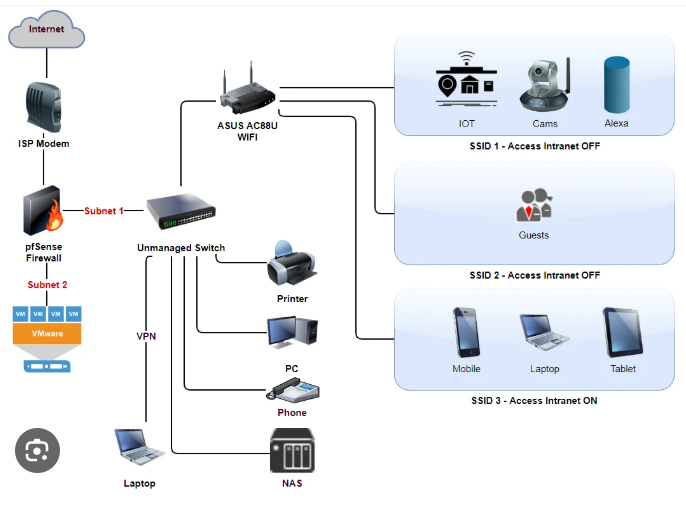
Key Components of the Internet
| Component | What It Does |
| Client | Your device (phone, laptop, etc.) |
| Server | Stores and delivers websites or data |
| ISP | Connects you to the internet (e.g., BT, Virgin Media) |
| Router | Sends and receives data in your home/office |
| DNS | Translates website names into IP addresses |
Want to understand these devices better?
Networking Devices: Modem, Router, Switch
Internet vs Intranet
| Feature | Internet | Intranet |
| Access | Public, global | Private, internal (within companies) |
| Users | Everyone with internet access | Limited to employees or members |
| Example | Google, YouTube, Wikipedia | School or company portals |
The intranet is like a mini private version of the internet, used inside businesses or schools.
Read more on network types:
LAN, WAN, MAN Explained
Visual Example: Internet in Action
You → [Router] → [ISP] → [DNS Server] → [Web Server] → Website appears on your screen!
Still curious about how websites load or what DNS does?
Leave a comment below — and I’ll break it down for you!